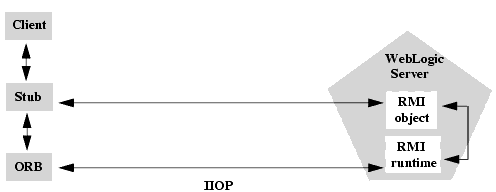
RMI-IIOP(RMI オーバー IIOP)とは、CORBAシステム上のJava RMIインタフェースを指す。
概要
この標準は、CORBA の利点を保ちつつ、CORBA アプリケーションの開発を単純化するべく作成された。RMI-IIOP は、CORBA 構造体、共用体、シーケンス、配列、文字列などを置換するコンテナとして働く Object by Value の概念に基づいている(CORBAの項目を参照)。IDLは使われていない。代わりに自動的にデータ構造定義を推定し、リフレクション機構で必要なデータを集める。CORBA では転送すべきデータ構造ごとに補助的なクラスを生成する必要があるが、RMI-IIOP ではリモートオブジェクト向けに生成されたコードを使うだけでよい。生成すべきコード量が少ないため、メモリ使用量も減らせる。
CORBA と RMI-IIOP はどちらも通信規格の GIOP を使用している。RMI-IIOP のデータ構造について、必要ならばIDLを生成することも可能で、それを使って、RMI-IIOP と 純粋な CORBA アプリケーションの相互運用を行うことも可能である。
RMI-IIOP の最近のバージョンでは標準のサーバントクラスからサーバントを生成できる。これを使うと CORBA の ORB に手動で接続でき、Portable Object Adapter、Portable Interceptor、CORBA のネーミングサービスなどの各種 CORBA 機能に接続可能である。
Hello world の例
Java RMI-IIOP を実装したパッケージの標準的な名称は javax.rmi.CORBA である。
インタフェース
public interface MyServer extends Remote
{
// クライアントは self を第一引数に渡す。サーバはクライアント側
// にあるリモートメソッドを呼び出せる。これは要求処理に時間がかかる場合に
// 便利である。
void receiveRequest(MyClient client, String message) throws RemoteException;
}
public interface MyClient extends Remote
{
// このリモートメソッドはサーバから呼び出される
void receiveReply(String message) throws RemoteException;
}
クライアントとサーバの機能実装
public class MyServerImpl implements MyServer
{
void receiveRequest(MyClient client, String message) throws RemoteException
{
System.out.println("The client says: " message);
client.receiveReply("Yes, " message ", " message ", " message "...");
}
}
public class MyClientImpl implements MyClient
{
MyServer server;
public MyClientImpl(String Server_IOR, ORB orb)
throws Exception
{
server = (MyServer) PortableRemoteObject.narrow(
orb.string_to_object(Server_IOR), MyServer.class);
}
// これはリモートメソッド
void receiveReply(String message) throws RemoteException
{
System.out.println("And the answer is: " message);
}
// これはリモートメソッドではなく、ローカルメソッド
public void talk(String conversation)
{
server.receiveRequest(this, conversation);
}
}
RMI-IIOP 開発ツール(rmic)は上記2つのクラスを使い、リモート側で使われる2つのスタブとサービス側で使われる2つの Tie を生成する。つまり、スタブと Tie のペアがそれぞれクライアント側とサーバ側に置かれる。
サーバ機能開始に必要なコード
new Thread()
{
public void run()
{
try
{
// CORBA ORB の生成
MyServerImpl.orb = ORB.init(args, properties);
// ルート Portable Object Adapter を取得:
POA rootPOA = POAHelper.narrow
(MyServerImpl.orb.resolve_initial_references("RootPOA"));
// MyServerImpl にはサーバがサポートしなければならない
// メソッドの実装が含まれる。
MyServerImpl impl = new MyServerImpl();
PortableRemoteObject.exportObject(impl);
// Tie の構築。Tie はサーバントでもある。
// _MyServerImpl_Tie クラスは MyServerImpl から自動的に生成される。
Tie tie = new _MyServerImpl_Tie();
// この Tie の呼び出しターゲットを設定
tie.setTarget(impl);
// 対応する CORBA オブジェクトへの参照を取得:
org.omg.CORBA.Object object = rootPOA.servant_to_reference((Servant) tie);
// ルート POA の活性化
rootPOA.the_POAManager().activate();
// クライアントに渡す IOR URL を取得
String Server_IOR = MyServerImpl.orb.object_to_string(object);
MyServerImpl.orb.run();
// 文字列変数 Server_IOR の内容をどうにかしてクライアントに
// 転送しなければならない
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
クライアント機能開始に必要なコード
MyClient the_client;
new Thread()
{
public void run()
{
try
{
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, parameters);
the_client = new MyClientImpl(Server_IOR, orb);
POA rootPOA = POAHelper.narrow(desk.orb.resolve_initial_references("RootPOA"));
rootPOA.the_POAManager().activate();
// Tie 構築
Tie tie = new _MyClientImpl_Tie();
// 実装クラス(呼び出しターゲット)の設定
tie.setTarget(the_client);
// Tie を POA サーバントとして接続
org.omg.CORBA.Object object = rootPOA.servant_to_reference((Servant) tie);
// IOR 文字列を使ってWeb上でこのオブジェクトを探すことが可能
String IOR = desk.orb.object_to_string(object);
orb.run();
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
ORB スレッドが開始した後で、以下のコードを実行する:
the_client.talk("it is raining");
実行
最初にサーバ、次にクライアントがそれぞれ別のマシン上で開始される(同一マシンの別プロセスでもよい)。サーバは The client says: it is raining と表示する。クライアントは And the answer is: Yes, it is raining, it is raining, it is raining.. と表示する。
ここに示したコードはサン・マイクロシステムズの Java 1.5 と GNU Classpath 0.95 で動作する。
略語利用の法的問題
IIOP という略称はOMGの商標であり、利用には注意が必要である。このプロトコルは GIOP 上にあるため、GIOPを利用しているとした方がよい場合もある。これは間違いではないが、やや正確さを欠く(GIOP の実装は他にも様々存在する)。詳しくはGIOPを参照されたい。
外部リンク
- The official RMI-IIOP standard from the OMG group (direct download, .pdf, about 890 Kb).
- The official CORBA standard from the OMG group (direct download, .pdf, about 10 Mb).